Parents often come to us concerned about white spots on their baby’s milk teeth. The formation of white spots or streaks on newly forming teeth is not uncommon, but they shouldn’t be ignored. These formations are generally caused by three things – early signs of decay, dental fluorosis, or enamel hypoplasia.
What is fluoride?
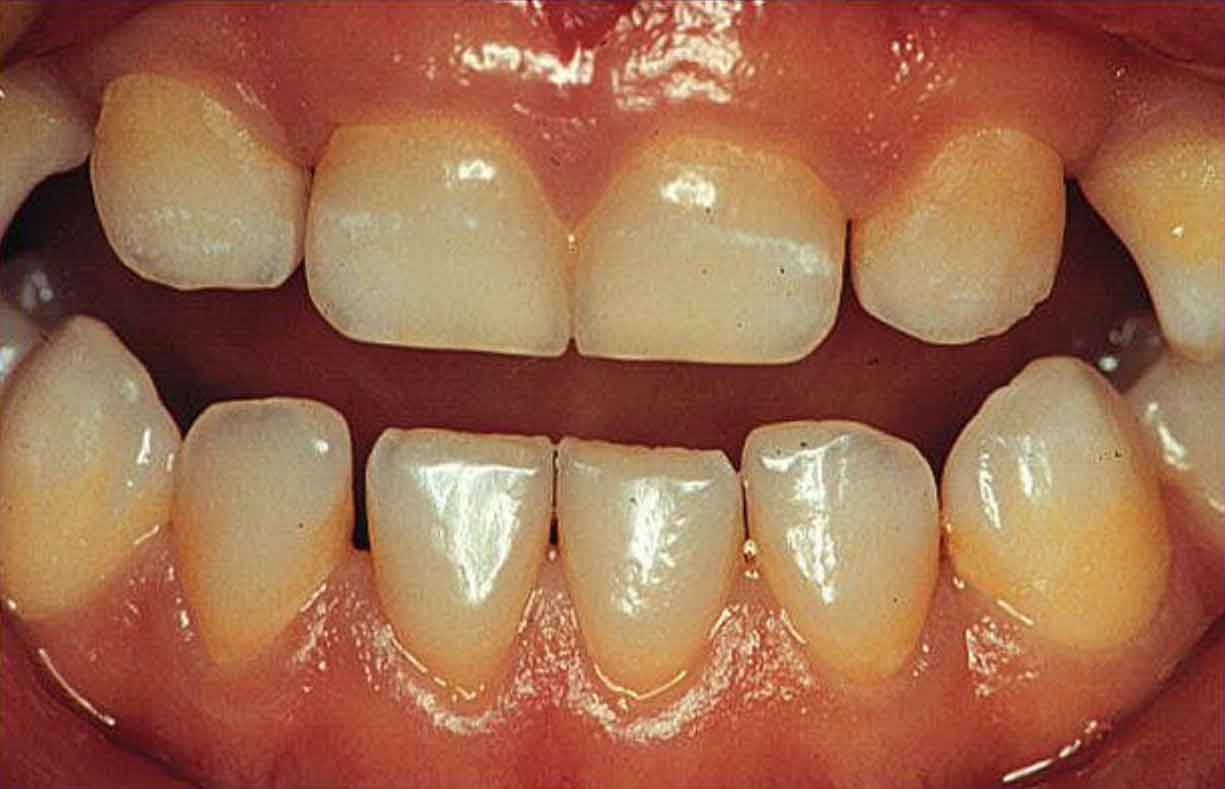
Normal, healthy baby teeth are white with smooth surfaces. Chalky white spots on your baby’s teeth can be a sign of early decay or weakened enamel. With proper oral hygiene and the right exposure to topical fluoride, this stage is reversible. If left untreated, it could lead to painful cavities (tooth decay or caries). If you notice white spots on your baby’s teeth, consult your pediatric dentist right away.
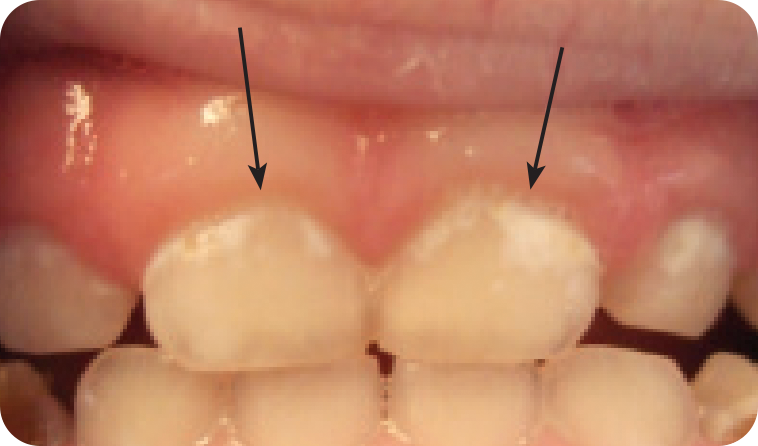
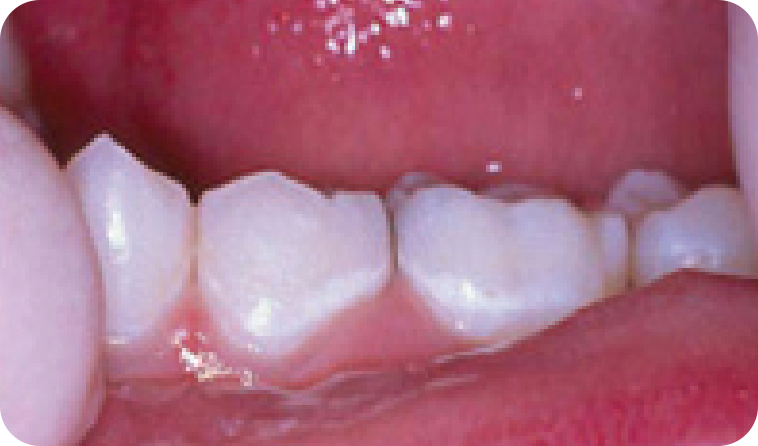
Chalky white spots on baby teeth (Photo credit: AAPD)
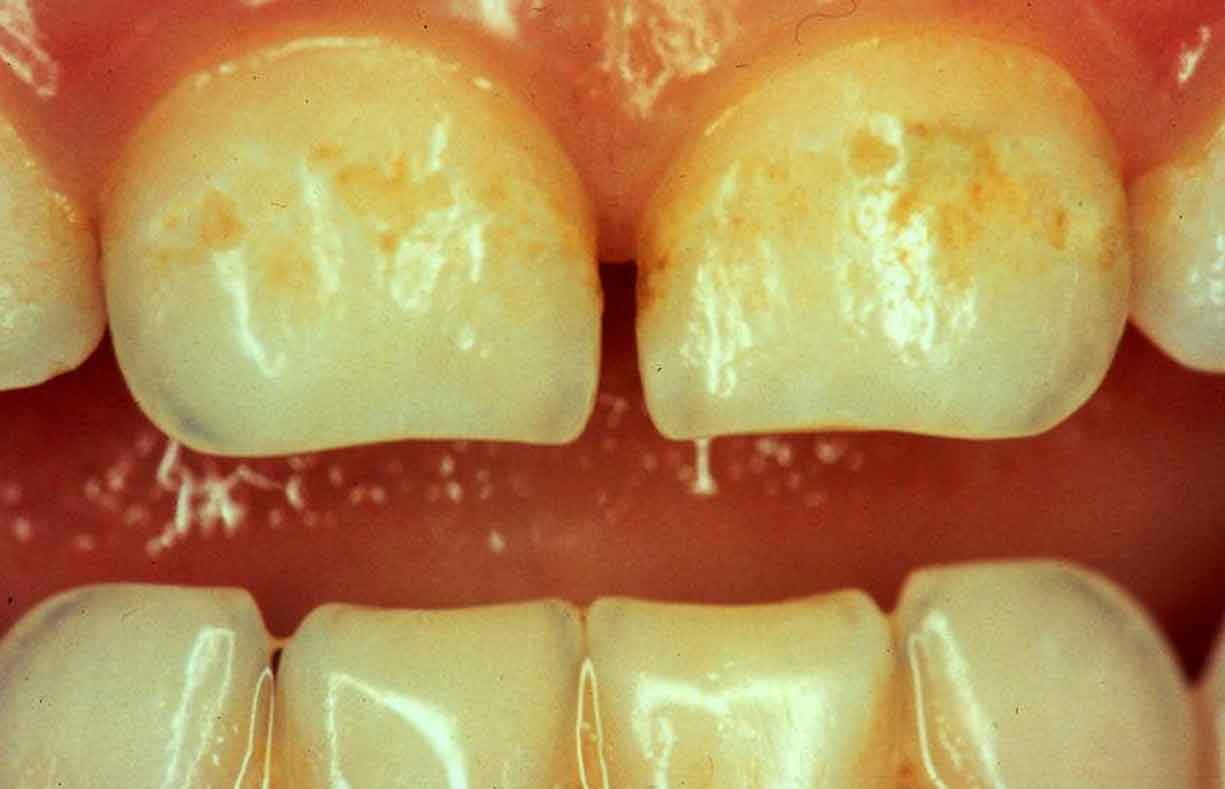
White streaks on children’s teeth could be a sign of dental fluorosis.
Fluorosis is the appearance of white streaks on the teeth as a result of excessive intake of fluoride. The chance of developing fluorosis exists while the teeth are still forming under the gums, until about age eight.
Fluoride is scientifically proven to protect our teeth from decay, and using the right amount is beneficial for both children and adults. It is important that we know the right amount of fluoride to use.
According to the recommendation of the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD), using no more than a smear or rice-size amount of fluoridated toothpaste for children less than three years of age may decrease risk of fluorosis. For children aged 3 to 6, use a pea-size amount.
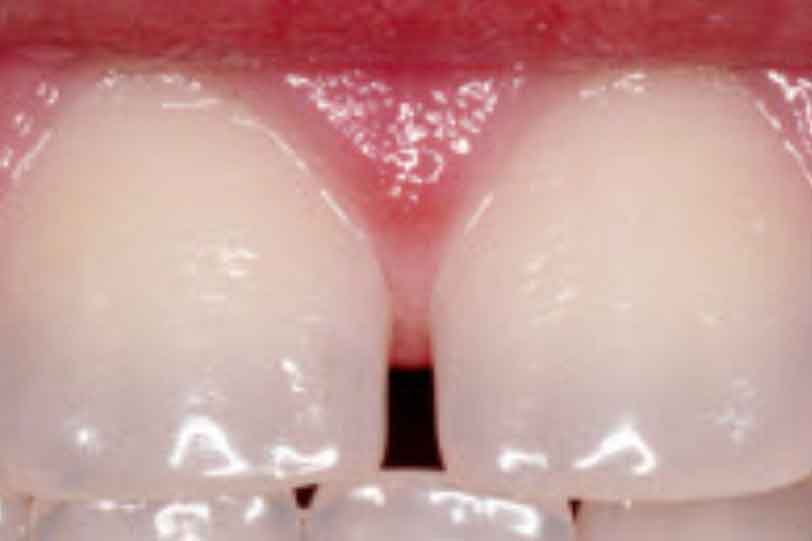
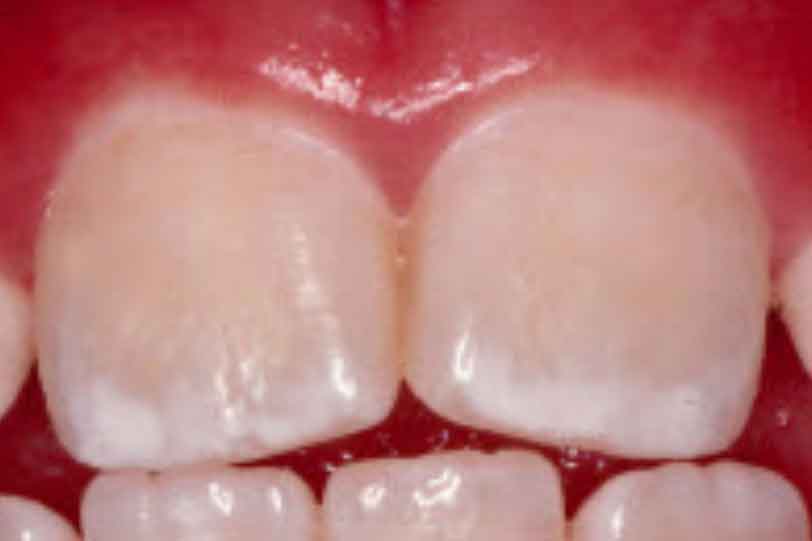
Normal versus mild fluorosis on baby teeth (Photo credit: AAP/HealthyChildren.Org)
White spots or pits on the teeth could be a sign of enamel hypoplasia.
Enamel hypoplasia is a developmental condition that occurs while the teeth are still developing. This condition results in thin or weak enamel often accompanied by white or yellowish spots, grooves, or pits.
Because of thin enamel, the teeth are fragile and may wear easily. The affected teeth may be more prone to tooth decay and tooth sensitivity. There are several treatment options available for enamel defects in children. Speak to your child’s dentist as soon as you see signs on your child’s teeth.
These are the three most common causes of white spots on children’s teeth. Moms and dads, if you notice these signs, don’t panic. Bring your child to a pediatric dentist to get the right assessment and treatment recommendations. Like most things, early intervention and getting the right information are keys to your child’s long term oral health.
Sources:













